Distributed using Kafka
This document describes additional details to the distribution scenario without Axon Server. Especially, it is used by one of the adopters of Polyflow (runs in production by a customer) using Apache Kafka (technically Azure Event Hubs) as an event distribution technology.
The following diagram depicts the task run from Process Application to the end user, consuming it via Tasklist API connected via Kafka and using Mongo DB for persistence of the query model.
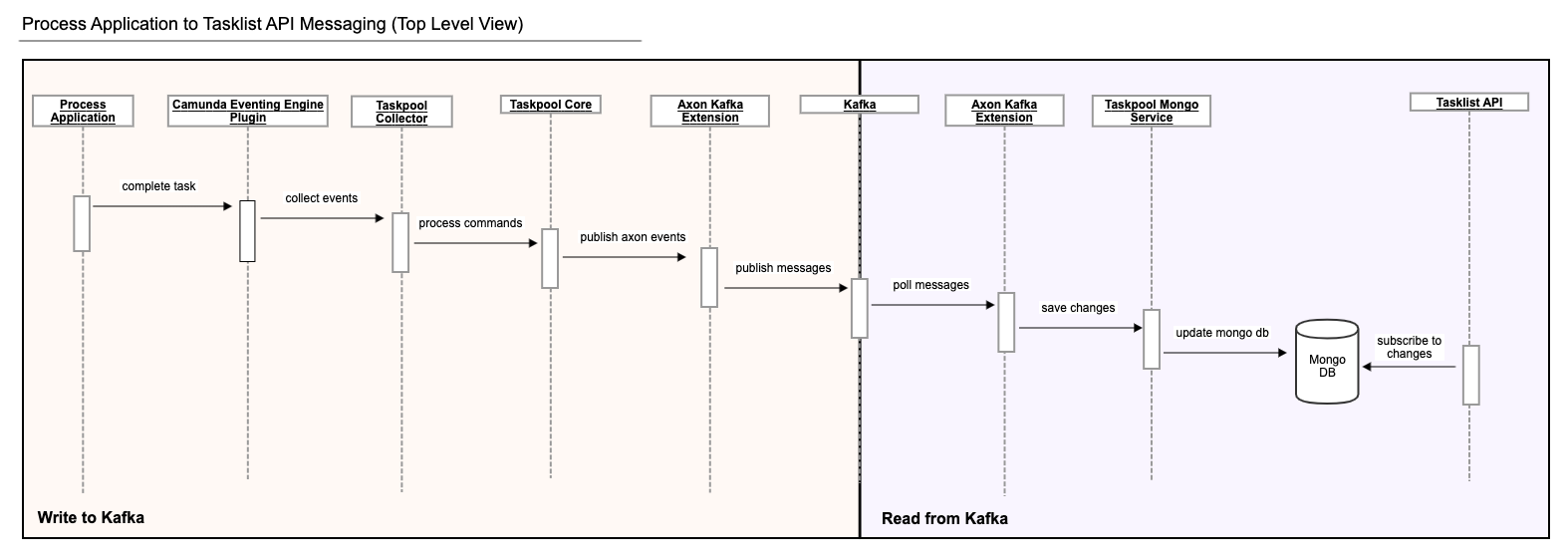
- The
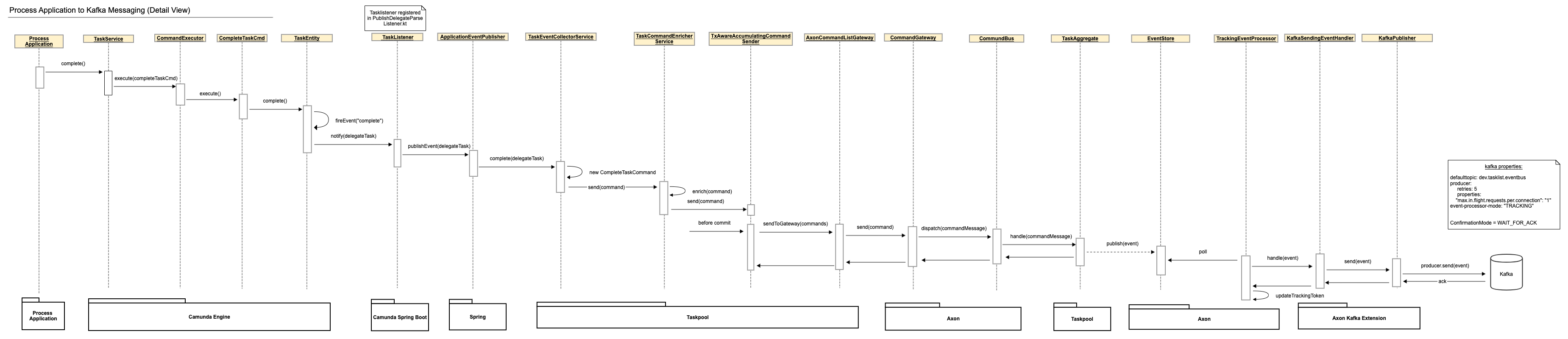
Camunda BPM Taskpool Collectorcomponent listens to Camunda events, collects all relevant events that happen in a single transaction and registers a transaction synchronization to process thembeforeCommit. Just before the transaction is committed, the collected events are accumulated and sent as Axon Commands through theCommandGateway. - The
Taskpool Coreprocesses those commands and issues Axon Events which are stored in Axon's database tables within the same transaction. - The transaction commit finishes. If anything goes wrong before this point, the transaction rolls back, and it is as though nothing ever happened.
- In the
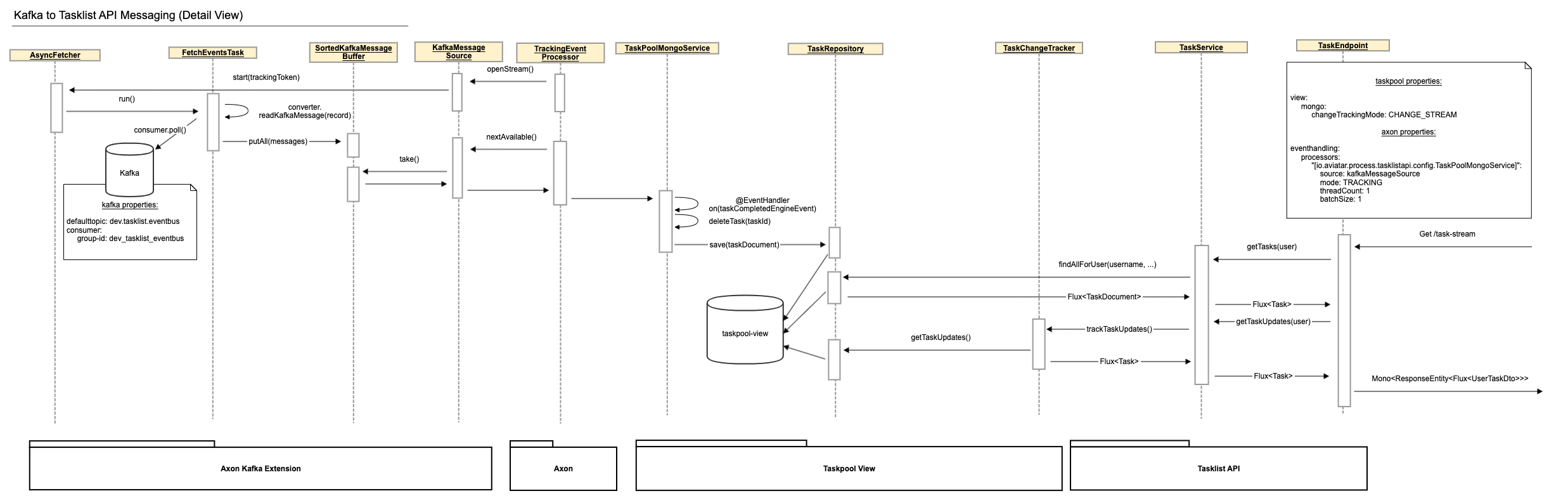
Axon Kafka Extension, aTrackingEventProcessorpolls for events and sees them as soon as the transaction that created them is committed. It sends each event to Kafka and waits for an acknowledgment from Kafka. If sending fails or times out, the event processor goes into error mode and retries until it succeeds. This can lead to events being published to Kafka more than once but guarantees at-least-once delivery. - Within the Tasklist API, the
Axon Kafka Extensionpolls the events from Kafka and another TrackingEventProcessor forwards them to theTaskPoolMongoServicewhere they are processed to update the Mongo DB accordingly. - When a user queries the Tasklist API for tasks, two things happen: Firstly, the Mongo DB is queried for the current state of tasks for this user and these tasks are returned. Secondly, the Tasklist API subscribes to any changes to the Mongo DB. These changes are filtered for relevance to the user and relevant changes are returned after the current state as an infinite stream until the request is cancelled or interrupted for some reason.
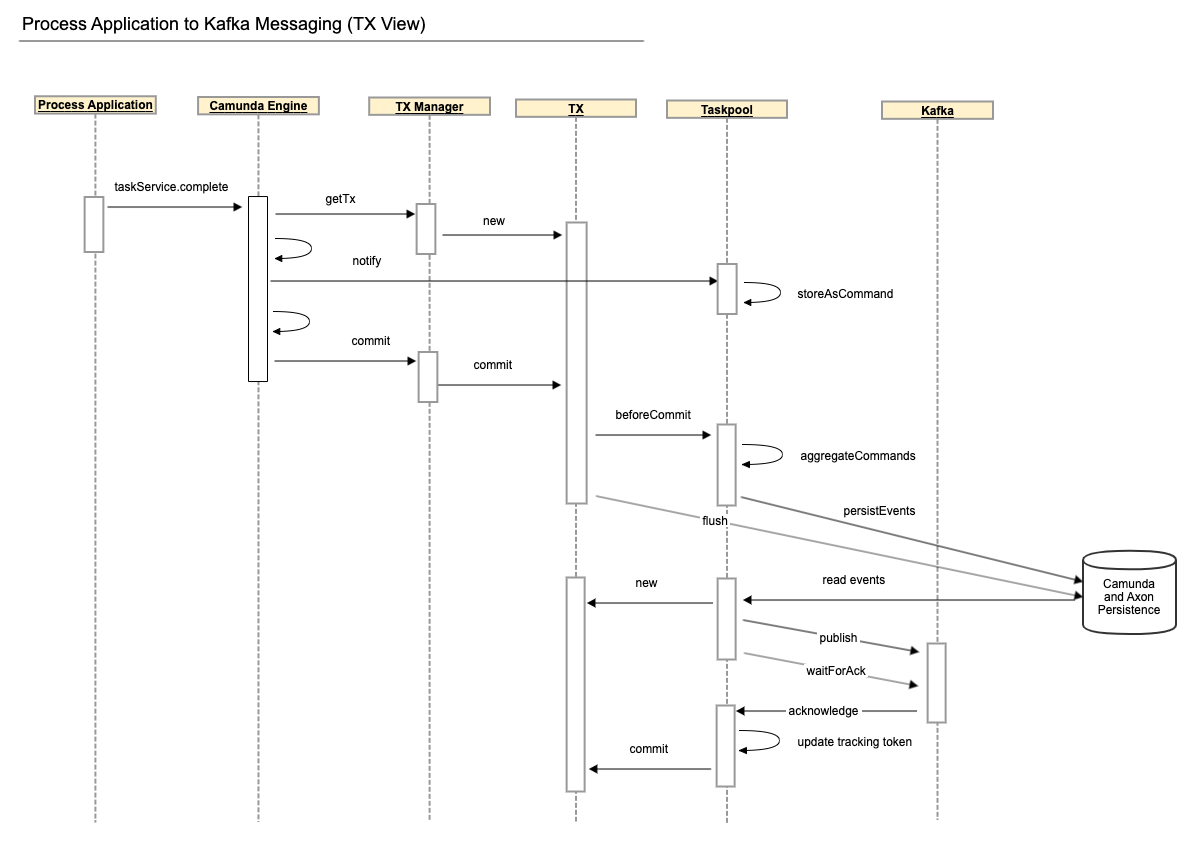
From Process Application to Kafka#
From Kafka to Tasklist API#
Last update:
May 5, 2023